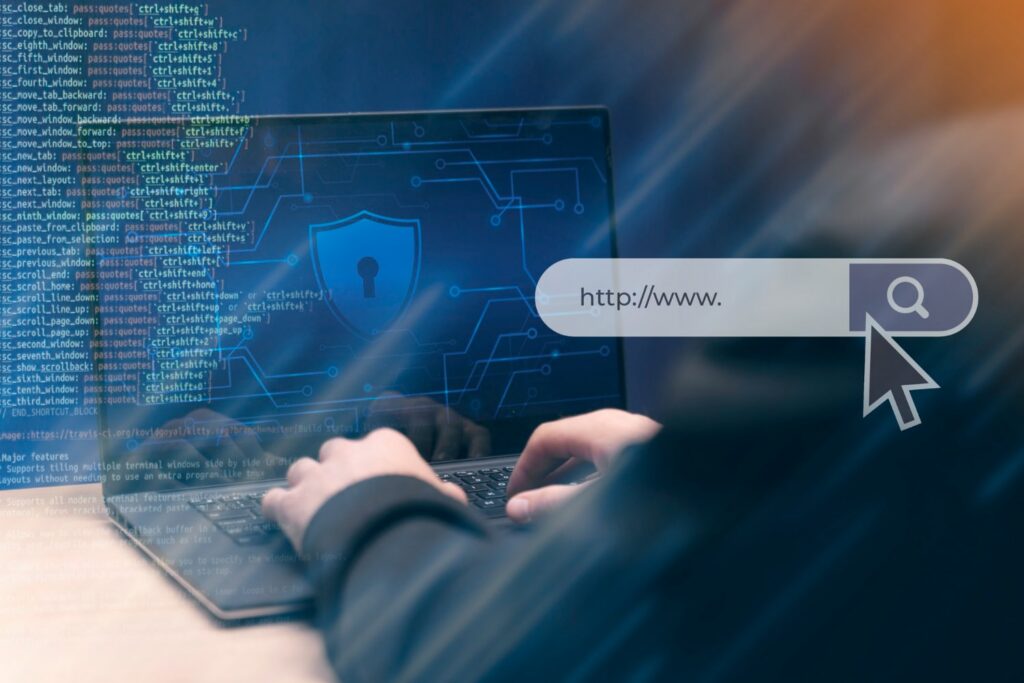
WordPress powers millions of business websites, blogs, and online shops, making it a frequent target for cyberattacks and malware. Effective security measures are critical to protect data, reputation, and customer trust.
1. Keep WordPress, Plugins, and Themes Updated
Outdated components are one of the main pathways for hackers. Regularly update your WordPress core and all plugins/themes to patch known vulnerabilities and stay ahead of new threats.
2. Use Reliable Hosting
Choose hosting providers with strong security protocols such as SSL certificates, account isolation, firewalls, and automated backups. Quality hosting is your first line of defense against most security risks.
3. Secure User Accounts: Avoid “admin” and Weak Passwords
Change the default “admin” username to something unique, and use strong, complex passwords. Enable two-factor authentication for all accounts to help prevent unauthorized access.
4. Limit Login Attempts
Install plugins like Limit Login Attempts Reloaded to prevent brute-force attacks – hackers won’t be able to endlessly guess passwords.
5. Use Trusted Plugins and Themes Only
Download only from WordPress.org or reputable marketplaces. Remove any unused or suspicious plugins – the fewer extensions, the lower your risk.
6. Install Dedicated Security Plugins
Leading WordPress security plugins in 2025 include:
- Wordfence Security (firewall, malware scanning, malicious traffic blocking)
- Sucuri Security (site monitoring, firewall, malware detection)
- SolidWP (formerly iThemes Security; login protection, backups, two-factor authentication)
- MalCare, All-In-One WP Security, Cloudflare – extra protection layers for both small and large websites.
7. Disable PHP Execution in Vulnerable Directories
Ensure folders like /wp-content/uploads/ do not permit execution of PHP files to prevent file upload exploits. Add a .htaccess file with:
text<Files *.php>
deny from all
</Files>
or enable this option via a security plugin such as Sucuri.
8. Manage User Permissions Carefully
Only grant admin access to users who truly need it. Assign the lowest level of privilege needed and regularly review user lists for old or unnecessary accounts.
9. Regularly Back Up Your Site
Set up automatic backups of your website and database so you can quickly restore if the worst happens.
10. Continuously Monitor Security
Set up alerts for suspicious activity, monitor for file changes, and keep learning about evolving cyber threats – ongoing awareness is vital.
Conclusion
WordPress can be highly secure if you follow core principles: keep everything updated, use strong security plugins, regularly back up your data, and educate your team on cyber threats. Implementing this checklist will dramatically reduce your chances of hacks and data loss.
Stay Ahead with the Latest Tech & Business Insights!
Get trending news, expert tips, and industry updates—delivered straight to your inbox.
"*" indicates required fields